May 2, 2025
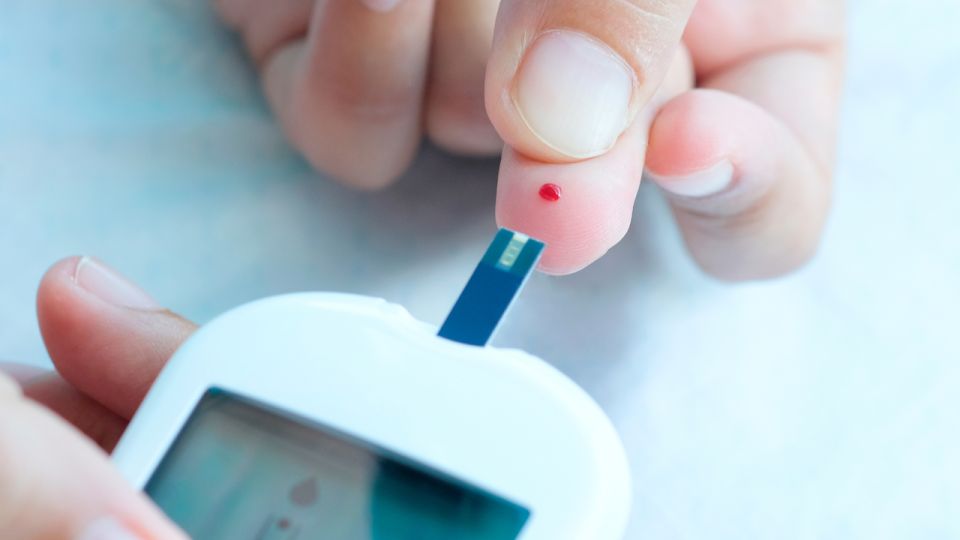
SEOUL – The number of Koreans in their 20s and 30s diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes has more than doubled in a decade, with approximately 370,000 people in this age group now living with the disease, a recent study shows.
According to research published in the Diabetes and Metabolism Journal of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2.02 percent of Koreans aged 19-39 had Type 2 diabetes in 2020, up from 1.02 percent in 2010. The increase of diabetes cases among young adults is especially noticeable among those in their 30s, where the rate increased from 2.9 percent to 3.9 percent in the same period.
Type 2 diabetes refers to a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels stemming from the body’s inability to use insulin correctly, which can eventually cause damage to the eyes, kidneys, nerves and heart. Obesity and lack of physical exercise are among factors linked to diabetes, along with family history, poor diet and certain medications.
The researchers found that a significant number of those with Type 2 diabetes had a high body mass index. Some 67.8 percent of young adults with diabetes here had a BMI of 25 kilograms per square meter, while 31.6 percent had a BMI of at least 30. BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight (in kg) by their height in meters squared.
A substantial number of young adults with diabetes also had other metabolic conditions, including dyslipidemia (79.8 percent), fatty liver (78.9 percent) and high blood pressure (34.2 percent). Several cases of heart-related diseases were also found in diabetic patients in the 19-39 age group.
Researchers noted that the recent rise of Type 2 diabetes among young adults here reveals a need for government attention, such as programs tailored specifically for young vulnerable groups and systems to support those with obesity.
South Korea has recently seen increases in the diabetes prevalence rate. The Health and Insurance Review and Service report in November revealed that 7.46 percent of the population, or 3.82 million, have diabetes. The number of people with diabetes here increased by 18.6 percent between 2019 and 2023, with male patients rising by 19.6 percent and female patients by 17.3 percent in the same period.
Despite the rising number of people with diabetes in their 20s and 30s, studies have shown that only one-third of such cases are being treated. According to the Diabetes Fact Sheet 2024 by the Korean Diabetes Association, 35 percent of diabetes patients in their 20s and 30s were receiving treatment.